


Dotted-Decimal Notation
To make Internet addresses easier for human users to read and write, IP addresses
are often expressed as four decimal numbers, each separated by a dot. This format
is called "dotted-decimal notation."
Dotted-decimal notation divides the 32-bit Internet address into four 8-bit (byte)
fields and specifies the value of each field independently as a decimal number
with the fields separated by dots. Figure 5 shows how a typical /16 (Class B) Internet
address can be expressed in dotted decimal notation.
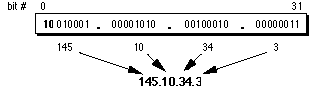
Figure 5: Dotted-Decimal Notation
Table 1 displays the range of dotted-decimal values that can be assigned to each
of the three principle address classes. The "xxx" represents the host-number field
of the address which is assigned by the local network administrator.

Table 1: Dotted-Decimal Ranges for Each Address Class
Unforeseen Limitations to Classful Addressing
The original designers never envisioned that the Internet would grow into what it
has become today. Many of the problems that the Internet is facing today can be
traced back to the early decisions that were made during its formative years.
-
During the early days of the Internet, the seemingly unlimited address space allowed
IP addresses to be allocated to an organization based on its request rather
than its actual need. As a result, addresses were freely assigned to those who asked
for them without concerns about the eventual depletion of the IP address space.
-
The decision to standardize on a 32-bit address space meant that there were only
2 32 (4,294,967,296) IPv4 addresses available. A decision to support a slightly
larger address space would have exponentially increased the number of addresses
thus eliminating the current address shortage problem.
-
The classful A, B, and C octet boundaries were easy to understand and implement,
but they did not foster the efficient allocation of a finite address space. Problems
resulted from the lack of a network class that was designed to support medium-sized
organizations. A /24, which supports 254 hosts, is too small while a /16, which
supports 65,534 hosts, is too large. In the past, the Internet has assigned sites
with several hundred hosts a single /16 address instead of a couple of /24s addresses.
Unfortunately, this has resulted in a premature depletion of the /16 network address
space. The only readily available addresses for medium-size organizations are /24s
which have the potentially negative impact of increasing the size of the global
Internet's routing table.
The subsequent history of Internet addressing is focused on a series of steps that
overcome these addressing issues and have supported the growth of the global Internet.
Additional Practice with Classful Addressing
Please turn to Appendix B for practical exercises to further
your understanding of Classful IP Addressing.








