


CIDR is Similar to VLSM
If CIDR appears to have the familiar look and feel of VLSM,
you're correct! CIDR and VLSM are essentially the
same thing since they both allow a portion of the IP address space to be recursively
divided into subsequently
smaller pieces. The difference is that with VLSM, the recursion is performed on the
address space previously
assigned to an organization and is invisible to the global Internet. CIDR, on the
other hand, permits the recursive
allocation of an address block by an Internet Registry to a high-level ISP, to a
mid-level ISP, to a low-level ISP, and
finally to a private organization's network.
Just like VLSM, the successful deployment of CIDR has three prerequisites:
Another important benefit of CIDR is that it plays an important role in controlling
the growth of the Internet's
routing tables. The reduction of routing information requires that the Internet be
divided into addressing domains.
Within a domain, detailed information is available about all of the networks that
reside in the domain. Outside of an
addressing domain, only the common network prefix is advertised. This allows a single
routing table entry to
specify a route to many individual network addresses.

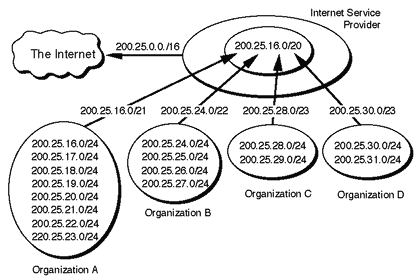
Figure 31: CIDR Reduces the Size of Internet Routing Tables
Figure 31 illustrates how the allocation described in previous CIDR example helps reduce the size of the Internet routing tables. Assume that a portion of the ISPs address block (200.25.16.0/20) has been allocated as described in the previous example. Organization A aggregates 8 /24s into a single advertisement (200.25.16.0/21), Organization B aggregates 4 /24s into a single advertisement (200.25.24.0/22), Organization C aggregates 2 /24s into a single advertisement (200.25.28.0/23), and Organization D aggregates 2 /24s into a single advertisement (200.25.30.0/23). Finally, the ISP is able to inject the 256 /24s in its allocation into the Internet with a single advertisement - 200.25.0.0/16!
It should be mentioned that route aggregation via BGP-4 is not automatic. The network
engineers must configure each router to perform the required aggregation. The
successful deployment of CIDR will allow the number of individual networks on
the Internet to expand, while minimizing the number of routes in the Internet routing
tables.